728x90
Top Interview Questions 의 Easy Collection에 있는 문제입니다.
https://leetcode.com/explore/interview/card/top-interview-questions-easy/
Explore - LeetCode
LeetCode Explore is the best place for everyone to start practicing and learning on LeetCode. No matter if you are a beginner or a master, there are always new topics waiting for you to explore.
leetcode.com
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
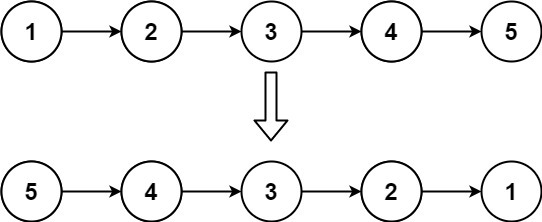
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
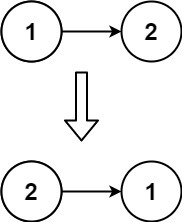
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
- -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
Follow up: A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
Code:
ver1. iterative한 풀이
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev = None
while head:
# ex) [range(1,6)]: 1을 맨뒤로, 2를 4번째로, .., 5를 첫번째로 옮기는 과정
# in-place가 아니고, prev라는 새로운 ListNode를 만들어 반환
curr = head # 가장 앞에 있는 노드를 대입
head = head.next # 그 다음 노드부터 시작하는 리스트노트를 head에 대입
curr.next = prev # curr의 next를 prev로 삼고
prev = curr # curr를 prev에 대입 => 현재 head의 가장 앞에 있던 노드를 맨 앞 노드로 삼는 리스트노드가 됨
return prev
ver2. recursive한 풀이
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next: # listnode가 없거나, element 1개인 경우
return head
node = self.reverseList(head.next) # 재귀를 통해 가장 마지막에 있는 node 가져옴
head.next.next = head # 5->4, 4->3, ..., 2->1 이렇게 점차로 대입
head.next = None
return node
728x90
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Leetcode/Python] Valid Palindrome (0) | 2022.08.21 |
|---|---|
| [Leetcode/Python] Reverse String (0) | 2022.08.21 |
| [Leetcode/Python] Count Primes (0) | 2022.08.18 |
| [Leetcode/Python] 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (0) | 2022.08.17 |
| [Leetcode/Python] Validate Binary Search Tree (0) | 2022.08.16 |
